Ever wondered why does the stock market fall? Or what actually triggers a stock market crash?
The truth is, the stock market isn’t just numbers on a screen. It’s a living, breathing reflection of how millions of investors feel about the economy. When confidence is high, the market climbs.
But when fear or uncertainty kicks in, we see a stock market fall that can feel sudden and overwhelming.
If you’ve spent any time following the markets, you know they don’t move in a straight line. One moment, stocks are climbing; the next, they’re dropping, sometimes dramatically and without much warning.
For newcomers, this can be super alarming, even panic-inducing.
But what’s really behind these drops?
Is it just technical stuff or something bigger?
In this blog, we’ll break down the many reasons why markets fall, from economic changes to investor psychology.
We’ll also talk about how you can stay cool when things get shaky, avoid common mistakes, and make the most out of market corrections.
What is a Stock Market Fall?
A stock market fall refers to a significant decline in the overall prices of stocks traded on a stock exchange over a period of time. It means that the value of shares representing ownership in companies drops, leading to a decrease in the market’s total value, often measured by major stock indices like the S&P 500, Dow Jones, or Nifty 50.
This decline can happen gradually or suddenly and is usually driven by a mix of factors like economic changes, political events, company performances, or shifts in investor sentiment.
When investors get worried about future profits or the health of the economy, they tend to sell their shares, which pushes prices down.
The bigger the drop and the faster it happens, the more serious the stock market fall is considered.
Sometimes, a stock market fall turns into a stock market crash, which is a very sharp and steep decline occurring over days or weeks, causing panic and widespread losses.
Difference between Stock Market Fall and Stock Market Crash
You can learn about the differences from the table below:
| Aspect | Stock Market Fall | Stock Market Crash |
| What it is | A noticeable decline in stock prices over days or weeks. It’s a drop but usually less severe. | A sudden, sharp, and massive drop in stock prices, often happening in just a few days. |
| Severity | Moderate drop, usually up to 10-15% in major indices. | Very steep drop, often 20% or more in a short time. |
| Duration | A stock market fall Can last several days to weeks, sometimes months. | Happens very quickly, often within days or a few weeks. |
| Investor Impact | May cause concern or caution but not widespread panic. | Causes panic selling, fear, and sometimes market shutdowns. |
| Examples from India | The gradual dips during the COVID-19 uncertainties in early 2020 before the crash. | The 2008 global financial crisis impact on Indian markets where Sensex fell over 50% within months. Also, the 2020 crash in March during the initial COVID lockdown panic. |
| Common Causes | Economic slowdowns, profit-booking by investors, sector-specific issues. | Major economic shocks, global financial crises, political upheaval, or sudden loss of investor confidence. |
Why the Stock Market Go Up and Down?
Before we jump into why the stock market falls, it’s important to know that ups and downs are just part of how the market works.
Think of the stock market like a busy marketplace where millions of people, from regular folks to big companies, are constantly buying and selling shares based on what they think will happen next.
This back-and-forth naturally makes prices go up and down, toying around with a possibility of the stock market fall.
You can check the Indian stock market graphs to see how the domestic market is performing:
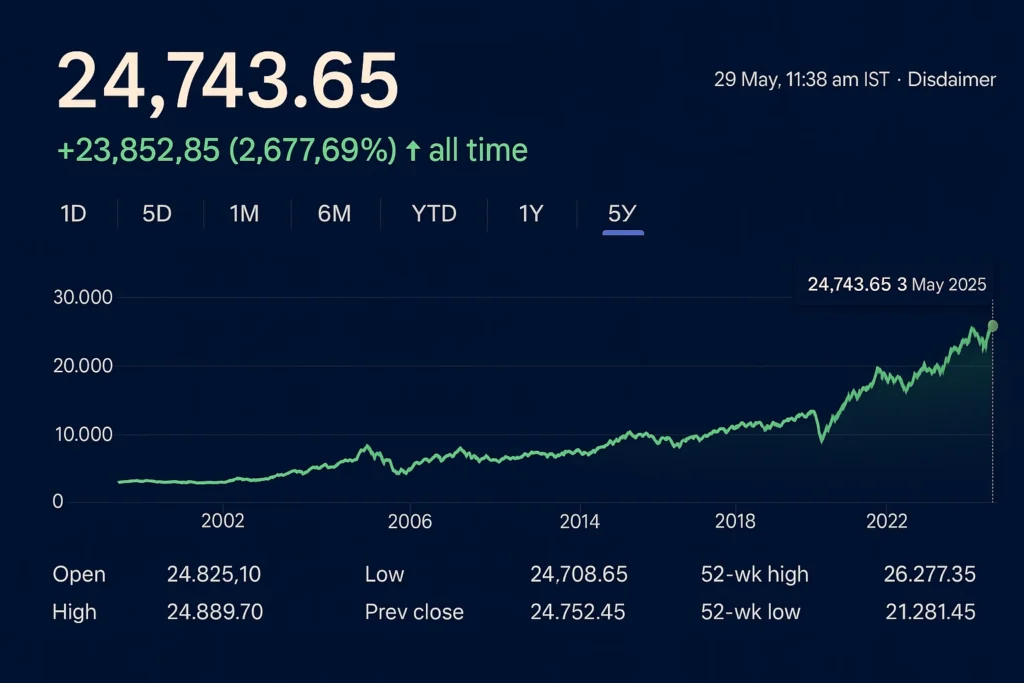
Data Source: NSE
Why does the Stock Price Change?
- Figuring Out Value: The market is always trying to figure out how much a company is worth, based on new news, reports, or events.
- Easy Buying and Selling: Because it’s easy to buy or sell shares, prices can change quickly depending on what people decide to do.
- Feelings Matter: Investors don’t just act on facts. Emotions like excitement, fear, hope, or worry can push prices up or down.
Truth 01: Volatility: The Inevitable Truth in a Stock Market Fall Scenario
What is Volatility in the Stock Market?
In the share market, volatility basically means how much the price of a stock or investment goes up and down over time. It shows how wild or calm the price movements are.
When volatility is high, prices can jump or drop a lot in a short time. When it’s low, prices tend to stay more steady.
You can think of it as the “bounciness” of a stock’s price; the more it bounces around, the higher the volatility.
Volatility isn’t all bad, as it lets investors buy low and sell high. The key is understanding why stock market falls and staying calm.
Truth 02: Economic Factors: Big Forces Behind Market Drops
The economy plays a huge role in how the stock market moves. When the economy is doing well, companies usually make good profits and stock prices go up. But if the economy shows signs of trouble, the market often takes a hit.
Here are some key economic reasons why markets fall:
- Interest Rates and Inflation: When central banks like India’s RBI or the US Federal Reserve raise interest rates to fight inflation, borrowing money gets more expensive for both companies and people. This can slow down business and reduce profits, which often causes markets to dip. For example, in 2022-2023, big interest rate hikes led to market corrections worldwide.
High inflation means prices keep rising, making things more expensive for everyone. This can eat into company profits and make people worry about slow growth combined with high prices (something called stagflation).
- Economic Slowdowns and Recession Fears: If the economy grows slower than expected, companies make less money, people lose jobs, and they spend less. This hurts stocks. Sometimes, just the fear of a recession is enough to make investors sell their shares and push the market down.
- Currency Changes: If the Indian rupee loses value, it gets more expensive for companies that rely on imports (like oil), cutting into their profits. Also, when the rupee weakens, foreign investors might pull their money out of India, which can drag the market down further.
- Government Debt and Borrowing: When the government borrows a lot, it can scare investors who worry about the country’s financial health. Too much borrowing can also limit how much private businesses can invest, which can hurt the market.
Truth 03: Corporate Performance: When Companies Disappoint
At the end of the day, stock prices reflect how well companies are doing and how much growth people expect from them. When companies don’t perform well, the market usually reacts fast.
Here’s why:
- Poor Earnings Reports: If a company’s quarterly profits come in below what experts expected, its stock price can drop quickly. This can also affect the whole market if it happens to big companies. For example: In May 2025, weak earnings from important sectors like IT and banking caused a big market sell-off.
- Profit Warnings: When companies warn that their profits will be lower than expected or cut their future forecasts, investors get worried and often sell their shares.
- Scandals and Bad Behavior: If a company is caught in a scandal like cheating on accounts or breaking rules, it hurts investor trust. This can cause a sudden drop in the company’s stock and sometimes affect the wider market. Like in 2009, the Satyam scam caused its stock crash and shook investor confidence.
- Problems in Specific Sectors: Sometimes, whole industries face trouble because of new rules, rising costs, or big changes in technology. When that happens, all companies in that sector can see their stock prices fall.
Truth 04: Global Events: How the World Shapes Indian Stock Markets
In today’s hyper-connected world, what happens in Washington, Beijing, or London doesn’t stay there. It ripples through to Mumbai’s Dalal Street in real time.
From foreign fund flows to inflationary pressures, global events directly impact Indian equities, investor sentiment, and even your SIP returns.
Global Economic Trends
US Federal Reserve Moves the Needle
The US Fed’s interest rate decisions send shockwaves through global markets. When they hike rates, Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) often pull capital out of emerging markets like India and shift to safer US bonds.
This was evident in 2022–23, when Fed tightening led to ₹80,000 crore+ worth of FII outflows, dragging down the Nifty and Sensex and causing a significant stock market fall.
Global Recessionary Fears
Slowdowns in key economies like the US, China, or EU reduce global consumption; especially for India’s top export earners like TCS, Infosys, Sun Pharma, and SRF Ltd.
During the 2023 slowdown in Europe, Indian IT stocks saw a steep correction (another hint of a significant stock market fall) due to weak client spending in BFSI and retail sectors.
Geopolitical Tensions
Conflicts and Global Uncertainty
War doesn’t need to be on Indian soil to impact Indian markets. The Russia–Ukraine war in 2022 led to panic selling across global indices, with Brent crude spiking above $120/barrel.
Indian stocks tanked, inflation rose, and sectors like aviation, paints, and logistics suffered due to input cost inflation.
- Example Closer to Home: Border skirmishes between India and China in Ladakh (2020) created temporary market volatility and spooked investors, showing how geopolitical events near home can also trigger sell-offs; which the investors register as a stock market fall in India event.
Trade Wars & Tariffs
Export-Heavy Sectors at Risk
India’s export sectors: IT, pharma, textiles, and auto components, are vulnerable to protectionist policies.
In April 2025, the US slapped new tariffs on generic drug imports, sending shockwaves across Indian pharma giants like Sun Pharma and Dr. Reddy’s, both of whom derive over 30% revenue from the US.
Global Health Crises
COVID Was Just the Beginning
The COVID-19 pandemic taught Indian investors the harsh lesson of global contagion.
Between February and March 2020, the Sensex crashed over 13,000 points as global lockdowns hit supply chains, consumer spending, and business activity across sectors.
- Lesson Learned: Indian markets don’t operate in isolation. A virus in Wuhan shut down malls in Delhi and factories in Pune.
Commodity Price Shocks
Crude Oil = India’s Inflation Trigger
India imports over 80% of its crude oil. So, when crude prices shoot up, like they did during the 2022 energy crisis, fuel costs, logistics, and inflation all spike.
This squeezes margins for companies in paint, FMCG, and auto sectors, triggering broader market corrections.
Gold Price Volatility
As a major importer of gold, any sharp price movement impacts India’s current account and rupee value.
When global uncertainties rise, Indians rush to buy gold, hurting the rupee and sometimes boosting certain gold stocks, but hurting the broader macro.
Truth 05: Government Policies and Regulatory Shocks
The stock market doesn’t just react to company news or the economy. It also gets majorly influenced by what the government does. Sometimes, these decisions can cause big and sudden drops in the market.
- Policy Changes: When the government announces its budget or changes rules about taxes, subsidies, or spending, it can directly affect certain industries. For example, higher taxes on specific goods or cuts in subsidies can hurt a company’s profits. Also, new rules like stricter environmental or data privacy laws might mean higher costs for businesses.
- Interest Rate Surprises: If the RBI suddenly hikes interest rates or changes its tone on money matters, the market can get spooked and react quickly. This is one of the most common reasons for stock market falls; however they do recover soon-after.
- Political Drama: Elections, unstable coalitions, or major policy flip-flops can make investors nervous. When there’s political uncertainty, markets often turn choppy. Upcoming Rajya Sabha Elections in 2025 can also bring along with them some instances of stock market falls.
- Shocking Announcements: Sometimes, unexpected moves like India’s demonetization in 2016, sudden bans, or court rulings can send shockwaves through the market and cause a quick stock market fall.
How Human Emotions Move the Market and Cause Stock Market Falls
The stock market isn’t just about numbers and charts. It’s also about people, and how they feel and how they react, especially when things get shaky.
Some human factors affecting the stock market falls are:
- Fear and panic selling: When stocks start dropping, many investors get scared. That fear quickly turns into panic, and people start selling in a hurry just to avoid more losses. This rush often makes the stock market fall even worse.
- Herd mentality: Ever heard the saying “everyone’s doing it”? That’s exactly what happens here. When people see others selling, they do the same, without thinking twice. The crowd effect pushes prices down even further.
- Overreacting to news: Sometimes, one scary headline is all it takes to send the market down. Even if nothing major has changed, the market might react way too strongly to the news.
- Loss aversion: People hate losing money more than they enjoy making it. That fear of loss can lead to bad decisions, like selling too soon or exiting the market at the wrong time.
- Margin calls: Some investors borrow money to buy stocks. But when prices fall, they may be forced to sell their shares to repay the loan, which adds even more pressure on the market, ultimately resulting in a stock market fall.
Technological and Systemic Risks Affecting Stock Market Falls
The stock markets today run heavily on technology. While this makes trading faster and more efficient, it also brings new risks that can sometimes lead to sudden market drops.
Algorithmic and High-Frequency Trading
In case of algorithmic trading (also known as “algo trading”), some trades happen through super-fast computer programs that react in seconds.
If too many of these systems sell at the same time, it can cause prices to fall very quickly, even if just for a short while. This is called a flash crash.
Technical Glitches and Infrastructure Failures
Sometimes, trading platforms or stock exchanges face bugs, system failures, or even cyberattacks.
These problems can stop trading or confuse investors, leading to panic in the market & cause a stock market fall.
Exchange and Settlement Risks
Once a trade is made, it needs to be completed through systems called clearinghouses.
If there’s a delay or error in this process, it can disturb the smooth working of the stock market and make people nervous.
Global Events and Their Real Impact on Indian Stock Market: Key Case Studies
The Indian stock market doesn’t operate in isolation. Events across the globe and within India’s borders have led to some of the most dramatic market movements, stock market falls and stock market crashes in history.
Below are some major case studies that highlight how sensitive Dalal Street is to real-world shocks:
1. COVID-19 Stock Market Crash (March 2020)
Trigger: Global pandemic and national lockdown
Market Impact of Covid-19
- Nifty 50 fell nearly 37% from around 12,000 in February to about 7,500 by late March.
- Sensex declined by over 13,000 points in just over a month.
Sectoral Impact
| Sector | Fall (%) |
| Aviation | ~60% |
| Hospitality | ~50% |
| Banking & NBFC | ~40% |
Key Reasons
- Global panic and institutional selling.
- Lockdown-driven halt in business activities.
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) withdrew over ₹65,000 crore in March 2020.
Investor Lesson
Black swan events are unpredictable. A diversified portfolio and adequate liquidity can help weather such extreme volatility.
2. IL&FS Default Crisis (September 2018)
Trigger: A leading NBFC defaulted on debt obligations worth ₹91,000 crore
Market Impact
- Nifty fell nearly 13% in three weeks.
- NBFC stocks and debt mutual funds took massive hits.
Sectoral Impact
| Segment | Typical Impact |
| Housing Finance | Severe |
| Private Banking | High |
| Mutual Funds | Moderate |
Key Reasons
- Erosion of trust in the NBFC sector.
- Liquidity freeze across credit markets.
- Panic-driven redemptions in debt mutual funds.
Investor Lesson
Beyond financials, governance and debt quality play a crucial role. High returns in debt instruments often come with high hidden risk.
3. Demonetisation Shock (November 2016)
Trigger: Sudden invalidation of ₹500 and ₹1,000 notes
Market Impact
- Sensex dropped nearly 6% on the first trading day after the announcement.
- Nifty dropped from around 8,700 to 7,900 in 10 days.
Sectoral Impact
| Sector | Short-Term Effect |
| Real Estate | Highly Negative |
| MSMEs | Credit Crunch |
| Fintech/Digital | Long-Term Positive |
- Cash-dependent sectors were hit hardest.
- Drop in consumer demand and liquidity.
- Uncertainty among investors and businesses.
Key Reasons
Investor Lesson
Policy risk is real. While digital segments gained in the long run, short-term damage to cash-driven sectors was unavoidable.
4. Global Financial Crisis (2008)
Trigger: Collapse of global financial institutions following the US subprime mortgage crisis
Market Impact
- Sensex crashed 60% from 21,000 in Jan 2008 to 8,000 in Oct 2008.
- Nifty followed a similar trajectory.
Sectoral Impact
| Sector | Approximate Fall |
| Banking | 50–70% |
| Infrastructure | 70%+ |
| Metals | 60% |
Key Reasons
Investor Lesson
- FIIs withdrew billions amid global panic.
- Indian markets affected despite sound domestic fundamentals.
- Severe credit crisis and recession fears.
Global contagion risk is significant. Monitoring FII behavior and global central bank actions is crucial, even for domestic investors.
5.Adani Group Rout (January 2023)
Trigger: Allegations by an international research firm regarding corporate governance and financial practices
Market Impact
- Group companies lost over $140 billion in market capitalization within weeks.
- Broader indices declined due to their weight in key benchmarks.
Sectoral Impact
| Segment | Estimated Decline |
| Conglomerates | 50–70% |
| Infrastructure | High |
| Renewable Energy | Very High |
Key Reasons
- Allegations led to loss of investor confidence.
- Sharp correction driven by FII exits and retail panic.
- Scrutiny from global and domestic stakeholders.
Investor Lesson
Corporate governance matters. Overexposure to a single group or theme can significantly increase portfolio risk.
Summary Table
| Case Study | Year | Key Lesson |
| COVID Stock Market Crash | 2020 | Stay diversified; manage risk in crisis |
| IL&FS Crisis | 2018 | Debt quality matters as much as returns |
| Demonetisation | 2016 | Policy decisions can shift market dynamics |
| Global Financial Crisis | 2008 | Global events heavily impact local markets |
| Adani Group Rout | 2023 | Corporate governance is non-negotiable |
What Should Investors Do During Market Falls?
Understanding why markets fall is great; but what really matters is how you handle it.
Here’s how you can stay smart when markets go red:
- Don’t Panic: Market ups and downs are totally normal. Take a deep breath and don’t make hasty decisions out of fear.
- Check Your Goals: If you’re investing for the long term (like 5+ years), a few bad weeks or months shouldn’t change your whole plan.
- Spread Your Risk: Don’t put all your money in one type of investment. Mix it up: stocks, bonds, gold, etc.; to reduce the impact of a fall.
- Don’t Try to Predict: Timing the market is a guessing game, and even pros get it wrong. It’s better to invest regularly (like through SIPs) than to keep jumping in and out.
- Spot Good Deals: During a fall, some strong companies may become cheaper. That’s a chance to invest in quality stocks at a discount.
- Keep Some Cash Handy: Have an emergency fund so you’re not forced to sell your investments when markets are down.
- Trust the Process: Markets have always bounced back. Stay patient, stay consistent.
- Ask for Help If You Need It: If you’re feeling confused or unsure, talk to a financial expert. It’s okay to ask for guidance.
Bottom Line
Stock market falls aren’t just random crashes. They’re reactions to real things like global events, economic trends, and investor emotions.
Whether it’s a Fed rate hike, a weak quarterly result, or a geopolitical shock, every dip has a story. And while it can feel scary in the moment, it’s important to remember that volatility is part of the game. In fact, it’s what creates opportunities for the patient and well-informed investor.
The key is to zoom out, not freak out. Don’t let a red market screen shake your long-term goals. Instead, treat it as a moment to reassess, rebalance, and maybe even buy quality stocks at a discount. Because history shows that every stock market fall eventually finds its rise.
The worst storms eventually clear, and who knows, the next bull run might just be stretching before it sprints 😉
So stay calm, stay curious, and don’t ignore the truths you’ve just learned. They’ll help you ride out the lows and prepare for the next high.
Disclaimer: Investments in securities market are subject to market risks. Read all the related documents carefully before investing. The securities are quoted as an example and not as a recommendation.
FAQs
Why is the market falling down?
Recent declines in Indian stock markets can be attributed to several factors:
Profit Booking: After significant rallies, investors often sell to lock in gains.
Weak Corporate Earnings: Subdued Q4 results, especially in financial and IT sectors, have dampened investor sentiment.
Global Cues: Rising U.S. Treasury yields and weak global markets have influenced domestic equities.
Foreign Investor Outflows: High valuations have led to some foreign investors pulling out funds.
What is the 7% rule in stocks?
The 7% rule advises investors to sell a stock if its price falls 7–8% below the purchase price. This strategy helps in limiting losses and preserving capital for future opportunities.
What is causing the stock market crash?
The stock market crash can result from a combination of factors:
Economic Indicators: Rising inflation, interest rates, or fiscal deficits.
Geopolitical Tensions: Conflicts or trade disputes affecting global trade.
Corporate Performance: Disappointing earnings reports.
Policy Changes: Sudden regulatory shifts or monetary policy adjustments.
What will be Sensex in 2025?
Forecasts vary as per different sources; projections from some state such:
Morgan Stanley: Projects Sensex at 82,000 by December 2025.
Reuters Poll: Analysts expect Sensex to reach 95,000 by end-2026.
Why is the market failing?
There are several factors causing a stock market fall. However, the markets may decline due to:
Overvaluation: Stocks priced higher than their intrinsic value.
Economic Slowdown: Reduced GDP growth or industrial output.
Policy Uncertainty: Ambiguity in government policies affecting investor confidence.
What to do when market is going down?
Stay Calm: Avoid panic selling.
Review Portfolio: Assess asset allocation and rebalance if necessary.
Continue SIPs: Systematic Investment Plans benefit from rupee cost averaging during downturns.
Seek Opportunities: Market corrections can offer buying opportunities in fundamentally strong stocks.
What is the biggest market crash in India history?
One of the most significant stock market crashes was the 1992 Harshad Mehta scam, where the Sensex plummeted by 12.7% in a single day.
Other notable crashes include the 2008 global financial crisis and the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic-induced crash.

