RBI Monetary Policy 2025 is in headlines again, and for good reasons. India’s economic landscape in 2025 is being shaped by a mix of global pressures and domestic resilience. While challenges like geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions persist, the economy has shown strong fundamentals.
The RBI projects real GDP growth at 6.5% for FY2025–26, reflecting cautious optimism amid global uncertainty.
On the inflation front, India recorded a retail inflation rate of 3.34% in March 2025, which is the lowest in nearly six years, driven by falling food prices and improved supply.
In response, the RBI reduced the repo rate to 6.00% in April 2025, signaling an accommodative stance to support growth. This move aims to ease borrowing costs, spur investments, and stimulate demand.
For stock market participants, these shifts in inflation and monetary policy are critical.
Lower inflation and interest rates generally boost equity sentiment, especially in interest-sensitive sectors. However, foreign investor behavior, global trade tensions, and central bank actions worldwide will continue to impact market flows.
In this blog, we explore how inflation and RBI’s monetary decisions are shaping market trends in 2025, and what that means for investors navigating this evolving financial environment.
Understanding Inflation and Its Current Trends
Definition and Causes of Inflation
Inflation is the general increase in prices of goods and services over time, reducing the purchasing power of money.
It can be caused by demand-pull factors (excess demand over supply), cost-push factors (rising production costs), and built-in inflation (adaptive expectations).
Current Inflation Scenario in India
As of March 2025, India’s retail inflation dropped to just 3.34%. That’s the lowest it’s been in five years! It’s also comfortably below the RBI’s target of 4%. This is actually the fifth month in a row that inflation has been cooling off, mainly because food prices; like eggs, spices, veggies, and pulses, have come down quite a bit.
Fuel and light prices did bounce back a little, but overall, consumer inflation is still pretty tame right now.
Here’s how India’s retail inflation has cooled over time (Jan 2024 – Mar 2025):
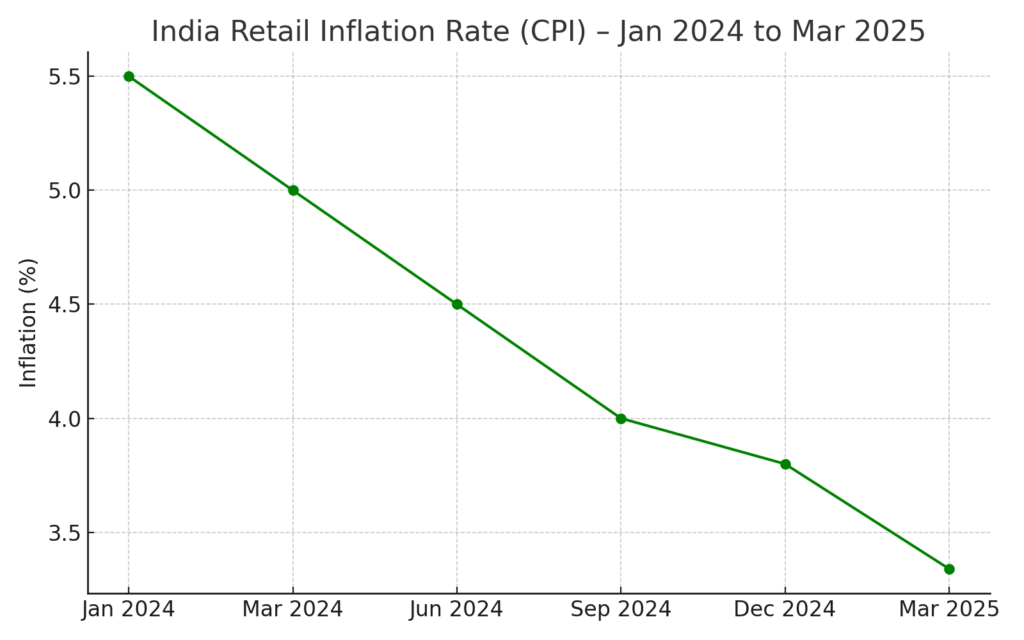
Sources: Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) & Times of India
Factors Contributing to Inflation Trends
- Agricultural Output: Above-average monsoon rains have boosted agricultural production, leading to lower food inflation.
- Global Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in global commodity prices, including crude oil, influence domestic inflation.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Improved supply chains and government interventions have helped stabilize prices.
These factors collectively contribute to the current low inflation environment, creating a conducive backdrop for monetary easing by the RBI.
RBI’s Monetary Policy in 2025
Overview of RBI’s Monetary Policy Tools
The RBI uses several tools to regulate the economy and control inflation:
- Repo Rate: This is the rate at which banks borrow money from the RBI. When the RBI increases this rate, borrowing becomes more expensive, which slows down spending and helps control inflation.
- Reverse Repo Rate: This is the rate at which the RBI borrows money from banks. It helps the RBI manage how much money is circulating in the economy.
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): This is the percentage of the bank’s deposits that they need to keep with the RBI. By changing this, the RBI controls how much money banks can lend out.
- Open Market Operations (OMO): This is when the RBI buys and sells government securities (like bonds) to manage how much money is available in the economy. It helps maintain liquidity and control inflation.
Recent Policy Decisions by RBI
In April 2025, the RBI cut the repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.00% and adopted an ‘accommodative’ stance to support economic growth amid global uncertainties.
This move reflects the RBI’s confidence in the easing inflation trajectory and its intent to stimulate domestic demand.
Inflation and Growth Projections
The RBI projects consumer price index (CPI) inflation at 4% for FY26 and real GDP growth at 6.5%, signaling a balanced approach to managing inflation while fostering economic expansion.
RBI’s gradual rate adjustments reflect a shift to an accommodative monetary stance. Here’s how India’s retail inflation has cooled over time (Jan 2024 – Mar 2025):
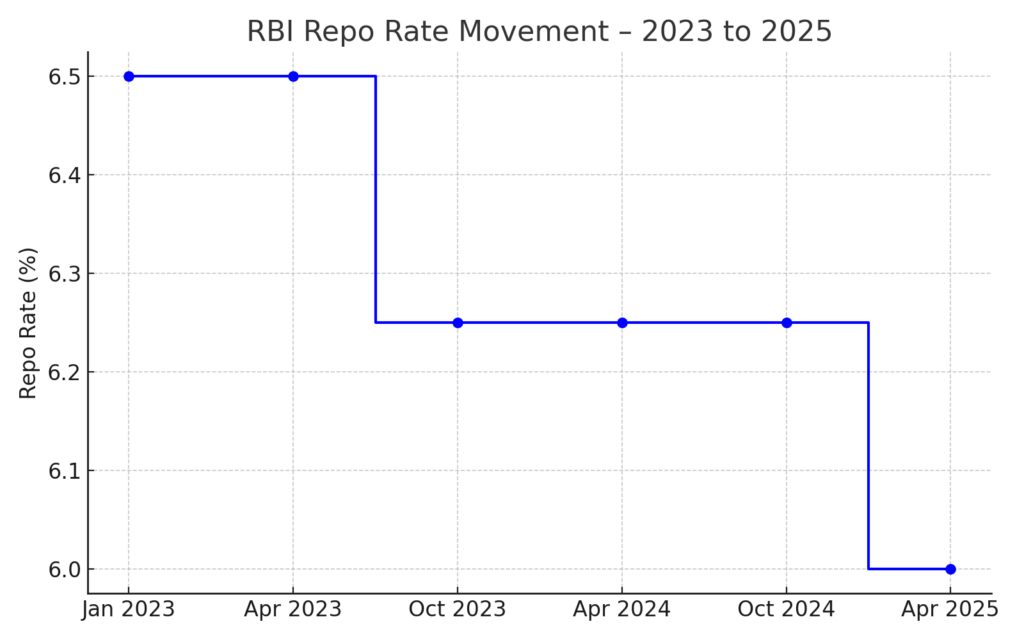
Sources: Reserve Bank of India Monetary Policy Press Releases & Press Information Bureau (PIB)
Rationale Behind Policy Decisions
The RBI’s rate cut aims to:
- Stimulate domestic demand by lowering borrowing costs.
- Counteract global trade tensions and their impact on growth.
- Support sectors affected by earlier monetary tightening.
By easing rates, the RBI hopes to reduce borrowing costs, encourage spending, and support sectors hit by earlier policy tightening.
With rates easing, investors and businesses are likely to find it cheaper to borrow and spend, marking a boost for market momentum.
Impact of RBI Policy Changes on the Indian Stock Market
Stock Market Performance in Early 2025
The Indian stock market faced a significant downturn, with the Nifty 50 index declining about 14% from its peak in September 2024.
This was driven by concerns over global recession fears, inflationary pressures, and foreign capital outflows:
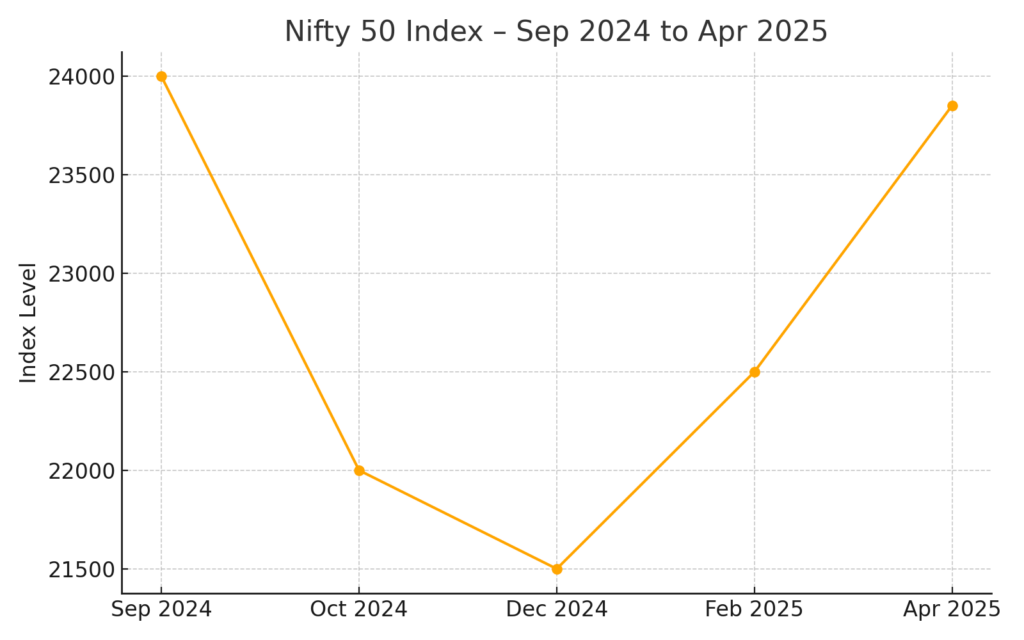
Sources: NSE India (Nifty Historical Data) & Investing.com: Nifty 50 Historical Closing Values
Sector-wise Analysis
| Sector | Impact Factors |
| Financial Services | Volatility due to sentiment shifts, macro headwinds |
| IT | Slow global tech spending, recession fears |
| Auto | High inflation, supply chain issues, high rates |
Investor Behavior
Foreign investors have withdrawn nearly Rs. 2,407 crore rupees from Indian equities since October 2024, reallocating funds to markets like China, reflecting global risk aversion and search for stability.
Market Recovery Prospects
As per some reports, analysts are forecasting a gradual recovery, with the Nifty 50 anticipated to rise over 6%, reaching 24,000 by mid-2025.
This positive outlook is supported by the RBI’s accommodative monetary policy and a decline in inflation.
Interplay Between Inflation, Monetary Policy, and Stock Market
Transmission Mechanism
Rising inflation prompts the RBI to adjust monetary policy, primarily through interest rate changes, which directly influence borrowing costs, corporate earnings, and consumer spending.
Lower inflation allows the RBI to cut rates, boosting liquidity and market confidence.
Interest Rates and Equity Valuations
Lower interest rates reduce the discount rate applied to future corporate earnings, leading to higher equity valuations.
Conversely, rising rates can dampen valuations by increasing borrowing costs and reducing profit margins.
Investor Sentiment
Monetary easing typically improves investor sentiment, encouraging greater market participation and higher stock prices.
The RBI’s accommodative stance in 2025 is expected to bolster confidence amidst global uncertainties.
Global Influences and External Factors
US Federal Reserve Policies
What happens in Washington doesn’t stay in Washington–the Fed’s policies ripple through Dalal Street too. Here’s how:
- The US Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions impact Indian markets through capital flows and currency valuation.
- Higher US rates can lead to capital outflows from India, pressuring the rupee and Indian equities.
Global Trade Tensions and US Tariffs
- US tariffs and potential trade wars exert pressure on the Indian rupee and inflation.
- India has responded by seeking to diversify trade partners and strengthen domestic industries to mitigate tariff impacts, aiming to shield its economy and markets from external shocks.
Foreign Investment Trends
- Global investor preferences shift with geopolitical and economic developments, influencing capital inflows or outflows.
- Maintaining investor confidence through stable policies is crucial for market liquidity and valuations
Future Outlook and Investment Strategies
Economic Projections
With inflation expected to remain within the RBI’s target range, further rate cuts are anticipated to support growth.
The RBI’s accommodative stance suggests a focus on sustaining economic momentum while monitoring inflation risks.
Investment Opportunities
| Sector | Rationale |
| Defensive Sectors | Healthcare, utilities, and consumer staples tend to perform well during economic uncertainty. |
| Growth Sectors | Infrastructure and real estate may benefit from lower interest rates and government initiatives. |
Risk Factors
Let’s talk about some risks we might face:
- A resurgence in inflation: This means prices might start rising again, which can make things more expensive for everyone. If inflation goes up too much, it could impact your savings and the overall economy.
- Global economic shocks: Things happening around the world, like a financial crisis or trade disruptions, can ripple through and affect India too. These shocks can mess with our economy in ways we can’t always predict.
- Policy missteps or sudden rate hikes: If the government or the RBI make the wrong policy decisions, like raising interest rates too quickly, it can slow down the economy. That could make borrowing more expensive and hurt businesses and consumers.
So, while there’s a lot of potential for growth, these are some things to watch out for.
What Does This Mean for Everyday Investors?
Inflation is finally cooling off, and the RBI has started cutting interest rates again.
Sounds like finance jargon? Here’s the simple takeaway: borrowing is getting cheaper, demand is picking up, and the overall environment is becoming more supportive for businesses to grow.
So what can investors like you take away from this?
1. Market mood is improving
When inflation is low and interest rates go down, the stock market usually responds well.
Sectors like banking, auto, and infrastructure often benefit in these kinds of conditions.
2. It’s a good time to check your portfolio
If most of your money is parked in conservative or defensive sectors, it might be worth rebalancing.
Growth-focused sectors could start gaining momentum, so you might want to be prepared for that shift.
3. Global events still matter
Even though things are looking good in India, what’s happening around the world—like US interest rate decisions or global trade issues—can still affect our markets.
Staying diversified is key.
4. SIPs and long-term investing can pay off
With inflation under control and growth policies in place, staying invested or even increasing your SIPs might work in your favour.
The market may not shoot up overnight, but it’s setting the stage for long-term gains.
5. Don’t rush—stay aware
This looks like a good phase, but risks still exist. Inflation could spike again, or global events could throw things off.
So stay updated, be smart with your decisions, and avoid reacting emotionally to short-term market moves.
Bottom Line
To wrap it up, 2025 looks promising for the Indian stock market, thanks to cooling inflation and the RBI’s supportive monetary policy. With lower interest rates, borrowing is cheaper, which could drive demand and investment in growth sectors.
While the overall mood is positive, it’s important for investors to stay vigilant. Global events and sudden policy shifts can still impact the market, so diversification remains key.
If you’re investing for the long-term, sticking to strategies like SIPs and focusing on sectors that benefit from lower rates could pay off.
That said, be mindful of risks—whether it’s inflation spiking again or global uncertainties affecting our market.
The future is looking brighter, but staying informed and making smart decisions will help you navigate the road ahead with confidence.
Disclaimer: Investments in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing.
FAQs
What is the outlook for the Indian stock market in 2025?
The Indian stock market is slowly finding its rhythm again in 2025. After a sharp correction in late 2024, the Nifty 50 has bounced back and is trading above 24,000 as of April.
This recovery has been supported by strong earnings from banks like ICICI and HDFC, easing inflation, and increased foreign investment.
With the Reserve Bank of India cutting interest rates to support growth, analysts believe the market could continue its upward journey, especially if global conditions remain stable.
How does RBI policy impact the stock market?
The RBI plays a major role in influencing the stock market. When it lowers interest rates, it becomes cheaper for businesses and individuals to borrow money. This tends to boost spending and investment, which benefits company earnings, and in turn, their stock price rises.
On the other hand, when the RBI raises rates to control inflation, it can slow down economic activity, which may hurt corporate profits and market sentiment. So, whenever the RBI makes a move, the market responds closely.
What is the monetary policy rate in 2025?
In its April 2025 monetary policy review, the RBI reduced the repo rate to 6.00%. This is the second rate cut this year, and it reflects the RBI’s effort to support growth in an environment where inflation is cooling and global uncertainties remain.
With borrowing costs coming down, the central bank is clearly focusing on stimulating domestic demand.
How does monetary policy affect the stock market?
Monetary policy affects everything from borrowing costs to investor mood. When the RBI cuts interest rates, it lowers the cost of loans for companies and consumers. This encourages businesses to expand and consumers to spend, which can lift company profits and boost stock prices.
More liquidity in the system also means more money flowing into the markets. However, if rates go up, borrowing becomes costlier, and companies may slow down on spending, which can weigh on stocks.
Will interest rates go down again in 2025?
There’s a good chance they might. With inflation under control and growth still a priority, many economists expect the RBI to cut rates further this year; especially if there are signs of economic slowdown or if global risks increase.
But any decision will depend on upcoming data and how external conditions unfold, particularly around global trade and interest rate moves by other central banks like the US Federal Reserve.
What is the inflation rate in India in 2025?
India’s inflation rate has been coming down steadily in 2025. As of March, retail inflation stood at 3.34%, the lowest in nearly six years. This has been helped by lower food prices and better supply chains.
For reference, the RBI’s comfort zone for inflation is around 4%, so we are currently in a very stable position. This drop in inflation is one of the main reasons why the RBI has been able to start cutting interest rates again.