If you are stepping into the market thinking intraday trading is a quick way to make fast money, pause for a moment. This Intraday Trading Guide 2026 is built with one clear purpose: to help beginners trade the Indian stock market using a simple, repeatable process instead of random bets driven by excitement.
In simple terms, intraday trading means buying and selling a stock on the same day. You do not carry positions overnight. Everything is closed before the market ends.
So why do most beginners struggle? Because they treat it like a shortcut. They overtrade. They ignore brokerage and taxes. They chase prices that are already moving. They use more leverage than they truly understand. In intraday trading, small mistakes do not stay small. They become expensive very quickly.
Instead of reacting to every price movement, this guide helps you build a clean routine for NSE intraday trading in 2026. What should you trade? When should you trade? Which time frames make sense? Which indicators actually help? How can you use VWAP setups without cluttering your charts?
The goal is not prediction. The goal is process, discipline, and consistency.
Let’s dive in!
Intraday Trading Basics
Intraday vs Delivery Investing: Same Stock, Different Game
You can buy the same NSE stock in two ways:
- Delivery: You buy it and hold it for days, months, or years. Your focus is business, valuation, long-term trends.
- Intraday: You buy and sell within the same day. Your focus is timing, liquidity, and risk control.
Intraday is less about “finding the best company” and more about “executing a plan in a liquid stock without blowing up.”
Suggested Read: How to Start F&O Trading? Unlock the Confidence to Trade Like a Pro
What is NSE Market Timing in India?
A lot of beginners don’t realize how much “time of day” affects intraday results.
NSE equity trading has a defined daily rhythm. The official NSE market timings page is the best reference for session details and close time.
Practical takeaway for beginners:
- The open is usually the most volatile.
- The middle hours can slow down.
- The last hour can become active again as traders square off.
Your strategy must respect the clock, because intraday is a game of timing.
The Real Risk in Intraday Trading Beginners Ignore
Even if your direction is right, you can still lose money because of friction:
- Brokerage and charges
- Taxes
- Bid-ask spread
- Slippage (your order fills at a worse price than expected)
- Overtrading (too many trades = too many costs)
Leverage makes this worse. With leverage, a small move against you can erase a day’s profit or more.
Beginner caution: SEBI-linked studies and reporting over recent years highlight that a very large majority of individual traders lose money in derivatives after costs, which is exactly why risk management discipline matters even for intraday thinking.
Also, SEBI’s margin frameworks emphasize upfront and timely collection of margins in cash and derivatives segments, which means “easy leverage” is not unlimited and risk controls are a regulatory priority.
Suggested Read: AI Trading Breakthrough Transforming the Indian Stock Markets
The Intraday Setup Checklist: Pre-Trade Routine
If you do nothing else, do this. A boring routine is what makes intraday survivable.
1. Pick the Right Stocks for Intraday
Choose stocks with:
- High liquidity: good volume, tighter spreads, smoother execution
- Cleaner movement: fewer random spikes, fewer “trap candles”
- Lower circuit-risk behaviour: avoid names that routinely hit upper or lower circuits or have sudden illiquidity
- Known catalysts: results, sector news, macro events
Beginner mistake: trading illiquid stocks because they “move more”.
Reality: they move more because they are easier to manipulate and harder to exit.
2. A Simple Daily Preparation Flow
Keep this simple and repeatable:
- Check the market mood
- Gap up day
- Gap down day
- Range day
- Mark yesterday’s key levels
- High
- Low
- Close
- Identify only 1 to 2 clean levels More levels = more confusion. You want fewer decisions, not more.
Best Time Frames for Intraday Trading
Common Intraday Time Frames and What They’re For
This is the simplest way to understand intraday time frames:
- 1D (Daily): Big picture and major support resistance
- 15-minute: Intraday bias and trend structure
- 5-minute: Entries and exits
- 1-minute or 3-minute: For experienced scalpers only. Very noisy.
If you’re new, avoid living on the 1-minute chart. It makes normal movement look like chaos.
The Top-Down Method Beginners Can Follow
This removes confusion:
- Step 1 (Daily): Mark big levels
- Step 2 (15m): Decide direction for the day
- Step 3 (5m): Execute entries and exits
You are not predicting. You are organizing information.
Best Time Frame Combos by Trading Style
- Beginner: 15m + 5m
- Intermediate: 30m + 5m
- Advanced: 15m + 3m or 1m (only with strict rules)
Think of time frames like lenses:
- Daily tells you the landscape.
- 15m tells you the route.
- 5m tells you where to step.
Best Indicators for Intraday Trading
The Rule: Indicators Confirm, They Don’t Predict
Indicators are filters. Price and volume are the reality.
If your setup does not work without 6 indicators, it is probably not a setup. It is confusion.
Core Indicators Beginners Should Start With
A) VWAP Indicator
VWAP stands for Volume Weighted Average Price. It is the average price of a stock for the day, calculated by giving more weight to prices where higher volume was traded. In simple words, it shows the average price at which most of the trading has happened during that session.
VWAP resets at the start of every trading day. Because of this, it is widely used as an intraday benchmark by traders and even institutions.
Why VWAP matters for intraday trading:
- If price is above VWAP and staying above it, buyers usually have the advantage.
- If price is below VWAP and staying below it, sellers usually have the advantage.
- On trending days, VWAP often behaves like dynamic support or resistance, where price reacts around it.
VWAP does not predict direction on its own. It helps you understand who is in control during the trading session and whether your trade is aligned with that control.
B) Moving Averages (EMA 20, EMA 50)
Exponential Moving Averages, or EMAs, are indicators that smooth out price data to show the short-term trend more clearly. The 20 EMA reacts faster to price changes, while the 50 EMA moves a little slower and shows a broader short-term trend.
For intraday trading, EMAs are best used as a trend filter.
- If price is above the EMA and the EMA is sloping upward, it often supports a bullish intraday bias.
- If price is below the EMA and the EMA is sloping downward, it supports a bearish bias.
The key is not to treat EMA as a magical entry signal. It does not tell you exactly when to buy or sell. It provides context about trend direction. You still need price action and proper risk management to make trade decisions.
C) Volume
Volume shows how many shares are being traded. In simple terms, it tells you how much participation is there in a price move.
Think of volume as fuel. A breakout without strong volume often fails because not enough traders are supporting that move. Price may cross a level, but if participation is low, the move can quickly reverse.
Volume is also useful during retests. If price comes back to a breakout level and volume starts drying up, it can be a clue that selling pressure is weak and the level may hold.
The goal is not to blindly trust every spike in volume. You are not worshipping volume. You are watching participation. Strong moves usually need strong participation. Weak participation often leads to weak follow-through.
D) RSI (One Simple Use-Case)
Many beginners use RSI the wrong way. They see “RSI is overbought” and immediately think the price has to fall. That is not how it works.
RSI, or Relative Strength Index, is a momentum indicator. It shows how strong recent price moves are on a scale of 0 to 100. When RSI is above 70, it is called overbought. But overbought does not mean the price will fall right away. In a strong uptrend, RSI can stay overbought for a long time.
- A better way to use RSI is for context, not prediction.
- Use RSI to spot weak breakouts. If price breaks to a new high but RSI is not showing strong momentum, the move may not be very strong.
- Look for simple divergence. If price makes a new high but RSI makes a lower high, it shows momentum is getting weaker.
But remember, this is only a warning sign. It is not an automatic signal to sell. Always wait for confirmation from price action and manage your risk properly.
E) ATR (Average True Range)
ATR stands for Average True Range. It measures how much a stock typically moves in a given period. In simple words, it tells you the average price range, not whether the price will go up or down.
- ATR is very practical for risk management.
- It helps you avoid placing stop losses that are too tight. If your stop loss is smaller than the stock’s normal movement, you may get stopped out even if your trade idea is correct.
- It also helps you avoid setting unrealistic targets. If a stock usually moves ₹10 in a session, expecting a ₹40 move in intraday trading may not be practical.
The key thing to remember is this: ATR is about distance, not direction. It does not tell you where price will go. It simply tells you how much the stock typically moves, so you can plan your stop loss and target more realistically.
Optional Indicators (Use Only If Needed)
Not every indicator needs to be on your chart. In fact, the more you add, the more confused you may become. These tools are optional and should be used only if they genuinely help your decision-making.
- Supertrend: A trend-following indicator that works well on strong trending days. It can help you stay aligned with the direction of the move instead of exiting too early.
- Bollinger Bands: Useful on range-bound days. They can support mean reversion logic, where price moves back toward the average after stretching too far.
- Pivot Points: Pre-calculated intraday levels that often act as support or resistance. They work better when combined with clear price action signals.
If your chart feels crowded or confusing, that is a warning sign. Remove indicators until the setup becomes clean and easy to read. A clear chart supports better decisions.
VWAP Strategies for Intraday Trading
The Heart of the Guide
A VWAP strategy works best when you stop treating VWAP like a simple line to buy or sell. Instead, treat it as a benchmark that needs confirmation from price and volume.
VWAP Strategy 1: Breakout and Retest
Core idea: Price breaks above VWAP, pulls back to it, holds, and then continues upward.
What to check before entry
- A clean close above VWAP
- Strong volume during the breakout
- A retest where price respects VWAP instead of falling back below it
Entry trigger
After the retest candle shows support, enter on confirmation. This could be the next candle moving higher or breaking the retest high.
Stop-loss
Place it below VWAP or below the retest low. Add a small buffer. ATR can help you define normal price movement.
Exit plan
- Book partial profits at 1:1 reward to risk
- Trail the remaining position using VWAP or EMA 20
Why this suits beginners
You are not chasing momentum. You wait for structure: breakout, retest, confirmation.
VWAP Strategy 2: Trend Day Ride
This works on clear trend days.
Conditions
- Strong directional movement
- Higher highs and higher lows in an uptrend
- Price respecting VWAP as support or resistance
Entry
Wait for a pullback toward VWAP. Look for rejection candles or volume picking up again.
Stop
Below VWAP with an ATR buffer.
Mindset
On trend days, VWAP acts like an anchor. You trade with the dominant direction.
VWAP Strategy 3: Mean Reversion
Idea: Price stretches far from VWAP, shows rejection, and moves back toward it.
Works best when
- Market is range-bound
- Trend strength is low
- Clear rejection at extremes
Be careful. Mean reversion fails badly on strong trend days.
Common VWAP Mistakes
- Treating every VWAP cross as a signal
- Ignoring volume and structure
- Using it on low liquidity stocks
- Overtrading because VWAP is always visible
VWAP is a framework, not a button.
Risk Management for Intraday
The Only Goal: Survive and Stay Consistent
Let’s be honest. Your first goal in intraday trading is not to double your money. It is to survive.
If you stay in the game long enough, you learn. If you blow up early, you learn nothing.
Before entering any trade, decide how much you are willing to lose if you are wrong. That is called risk per trade. Fix this amount in advance and keep it small. One losing trade should not disturb your confidence or your mindset.
Consistency comes from controlled losses, not big wins.
Stop-Loss Basics
There are two types of stop-loss:
- Hard stop: Placed directly in the system. It executes automatically. No debate.
- Mental stop: You promise yourself you will exit manually.
Most beginners break mental stops. That is why hard stops are safer.
Trading without a stop-loss is not confidence. It is gambling. The regret just comes later.
Position Sizing Made Simple
Two beginner-friendly methods:
Method 1: Fixed rupee risk per trade
- Decide a fixed amount, for example ₹500 per trade.
- If your stop-loss is ₹5 away, you can take 100 shares.
- Simple formula: ₹500 divided by ₹5.
Method 2: ATR-based stop
- Use ATR to place a stop that respects normal price movement.
- Then adjust your position size so your rupee risk stays the same.
This keeps your risk steady even when volatility changes.
Daily Rules That Protect Your Account
- Set a daily maximum loss. Stop trading once you hit it.
- Limit the number of trades per day. This prevents overtrading.
- No revenge trading. If you feel emotional, you are done for the day.
- Journal every trade in two lines:
- Why you entered
- Why you exited
- Why you entered
This is how real skill is built. Not by collecting profit screenshots, but by understanding your decisions.
A Simple Plan for Beginners to Start Intraday Trading
Copy, follow, repeat for 30 trading sessions
If everything feels confusing right now, simplify. Do not try five strategies at once. Start with one clean plan and stick to it for the next 30 trading sessions.
Instruments
Trade only liquid NSE large-cap stocks. High liquidity means smoother moves, tighter spreads, and fewer surprises.
Charts
- Use a 15-minute chart to understand the overall direction or bias.
- Use a 5-minute chart for your actual entry.
Indicators
Keep it minimal: VWAP + EMA 20 + Volume.
Nothing more. If your chart looks crowded, you are doing too much.
Setup Allowed
Only trade one setup: VWAP breakout and retest.
No random trades. No “this looks good.” Structure only.
Risk
Risk 1 percent of your capital per trade or use a fixed rupee risk.
One single trade should never damage your month. If it can, your size is too big.
Trading Window
Choose one to two focused hours. Trade only during that window.
Do not trade the entire day. More screen time does not create more edge. Most of the time, it creates more mistakes.
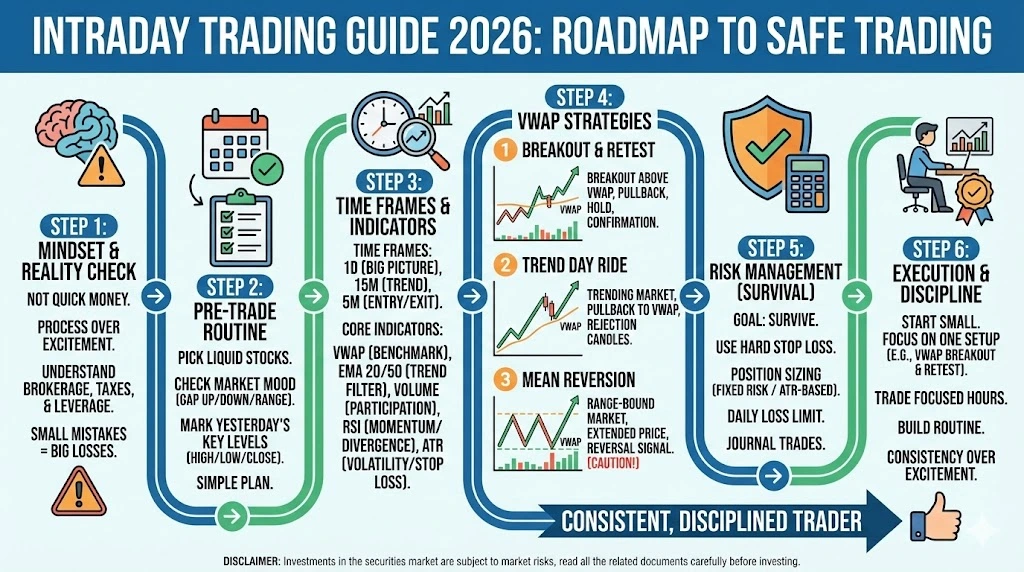
Conclusion: Keep It Simple, Keep It Structured
If you take only one thing from this Intraday Trading Guide 2026, let it be this: intraday trading is not about being right every time. It is about following a process every time.
The market will move whether you are prepared or not. Some days will trend beautifully. Some days will chop you around. That part you cannot control. What you can control is your routine, your risk, your position size, and your discipline.
You now have a clear framework.
You know which time frames to use.
You know which indicators actually matter.
You know how VWAP strategies work in real market conditions.
And most importantly, you know that risk management is not optional.
Do not try to master everything in one week. Pick the simple plan. Trade liquid NSE stocks. Follow one setup. Respect your stop-loss. Journal your trades. Repeat this for 30 sessions.
Skill in intraday trading is not built through excitement. It is built through repetition.
Treat this like a craft, not a lottery ticket. If you focus on process, consistency will follow. And in intraday trading, consistency is what separates participants from professionals.
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. The securities are quoted as an example and not as a recommendation.
FAQs
What is the best VWAP setting for intraday trading?
For intraday, the most practical VWAP setting is Session or Daily VWAP, because it resets each trading day and reflects where most volume traded in that session. Keep it simple: VWAP line on, bands optional. Treat it as a benchmark that needs confirmation from price structure and volume.
Which is the no. 1 indicator for intraday?
There is no single no. 1 indicator that works everywhere. Indicators help you filter and confirm, not predict. For most beginners, a clean combo like price action + volume + VWAP works better than hunting for a “magic” indicator. Keep charts readable and focus on execution and risk control.
Which timeframe is best for VWAP?
VWAP is session-based, so it works across intraday timeframes. For beginners, a solid approach is 15-minute for bias and 5-minute for entries, while using VWAP as the session benchmark. Very low timeframes like 1-minute can be noisy and trigger overtrading.
Can a beginner start intraday trading?
Yes, but start carefully. Begin with liquid large-cap stocks, one simple setup, and small fixed risk per trade. Be realistic about costs and the learning curve. Regulators and market studies repeatedly show most individuals lose money in high-frequency products after costs, so discipline matters more than confidence.

